Introduction
Un injecteur de plume is a specialized device that precisely delivers fluids into a process stream, ensuring optimal mixing and dispersion. These tools are crucial in industries where the accurate injection of chemicals, fuel, or other substances directly impacts system efficiency and product quality. Typically, quill injectors consist of a long, narrow tube that extends deep into a pipeline or vessel, delivering liquids at targeted locations to promote thorough blending.
In modern industrial applications, the role of quill injectors has become increasingly significant. Industries such as chemical manufacturing, oil refining, and water treatment rely heavily on these devices. They enable precise control over fluid flow rates and compositions, which is essential for maintaining rigorous safety and quality standards. Additionally, quill injectors help reduce waste and environmental impact by ensuring that only the necessary amount of chemicals enters the process stream.
Moreover, the precise operation of quill injectors minimizes the risks associated with handling hazardous materials. By improving safety and efficiency, these injectors contribute significantly to operational reliability and cost-effectiveness. This makes them an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern industry, driving innovations and improvements across numerous sectors.
Paramètres
| Nom | Système d’échantillonnage de piquants d’injection de produits chimiques dans les pipelines |
| Matériel | Acier inoxydable 304, acier inoxydable 316, DSS F51, acier au carbone A105N, Inconel 625 |
| Température de fonctionnement | -20±120 |
| Caractéristique | 1. Utilisation facile |
| 2. Haute précision, longue durée de vie | |
| 3. Haute efficacité, faible coût | |
| Paiement | TT/LC |
| Avantage | Tout d’abord, ils sont légers et flexibles. |
| Deuxièmement, une belle efficacité d’injection. | |
| Enfin un suivi précis de la localisation. |
Quill Injector Selection Model
| Modèle | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI | Plume d’injecteur chimique | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -Code | Bouchon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pxxx | Type | Matériel | Scellement Matériel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | Aucune demande | 0 | CS | 0 | Aucune demande | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Creux Corps de la prise | 1 | 316SS | 3 | DSS | 1 | Joint torique Viton / Garniture primaire en PTFE | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Corps de prise solide | 2 | 316LSS | 4 | INCONEL | 2 | HNBR | ||||||||||||||||||||
| –Code | Écrou d’injection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nxx | Taille de la connexion | Matériel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | c’est-à-dire aucune demande | 0 | i.e. CS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | c’est-à-dire 1/4" | 1 | c’est-à-dire 316SS | 3 | c’est-à-dire le DSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | c’est-à-dire 1/2" | 2 | c’est-à-dire 316LSS | 4 | c’est-à-dire INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| –Code | Injection Tube | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sxxx-Lx" | Taille de la connexion | Matériel | Buse | Taille de ligne (x") | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | Aucune demande | 0 | CS | 0 | c’est-à-dire aucune demande | La position la plus efficace pour l’injection se situe généralement au centre du tuyau | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | c’est-à-dire 1/4" | 1 | c’est-à-dire 316SS | 1 | c’est-à-dire ouvert | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | c’est-à-dire 1/2" | 2 | c’est-à-dire 316LSS | 2 | c’est-à-dire Quill | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | c’est-à-dire le DSS | 3 | i.e. Cap & Core | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | c’est-à-dire INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| –Code | Mamelon et valve (ou extrémité bride) du té | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Txx | Taille de la connexion | Matériel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | c’est-à-dire aucune demande | 0 | i.e. CS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | c’est-à-dire mamelon de 1/4 po | un | c’est-à-dire mamelon et valve de 1/4 po | 1 | c’est-à-dire 316SS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | c’est-à-dire mamelon de 1/2 po | b | c’est-à-dire mamelon et valve de 1/2 po | 2 | c’est-à-dire 316LSS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | c’est-à-dire mamelon 3/4" | c | c’est-à-dire mamelon et valve 3/4" | 3 | c’est-à-dire D SS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | c’est-à-dire 1" Mamelon | d | c’est-à-dire mamelon et valve de 1 po | 4 | c’est-à-dire INCONEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | c’est-à-dire bride 1/4" | e | c’est-à-dire 1/4" Bride d’extrémité de mamelon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | c’est-à-dire 1/2" Bride | f | c’est-à-dire 1/2 "Bride d’extrémité de mamelon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | c’est-à-dire bride 3/4" | g | c’est-à-dire 3/4 "Bride d’extrémité de mamelon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | c’est-à-dire bride de 1 " | h | c’est-à-dire 1" Bride d’extrémité de mamelon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Par exemple, SI-P221-N12-S122-L4"-T22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI:e.g. Sampling & Injection Assembly, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P221 : par exemple corps de connecteur solide en joint torique Viton 316LSS et garniture primaire en PTFE, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| N12 : par exemple, la taille de la connexion de l’écrou d’injection est de 1/4 "et Le matériau est 316LSS, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S122 :p. ex. injection Tube La taille de la connexion est de 1/4" et Le matériau est 316LSS. Le type de buse est des piquants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L4 » :Pour tuyau de 4 ». | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| T22 : Mamelon de la taille de la connexion en T est de 1/2", Le matériau de l’écrou est 316LSS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Understanding Quill Injectors
A quill injector is a precision device designed to introduce substances into a pressurized process stream or vessel. It features a slender tube that penetrates deep into pipelines, ensuring thorough mixing of substances without external equipment. This capability is pivotal in applications that demand high precision in fluid delivery and mixture quality, such as chemical dosing and fuel injection systems.
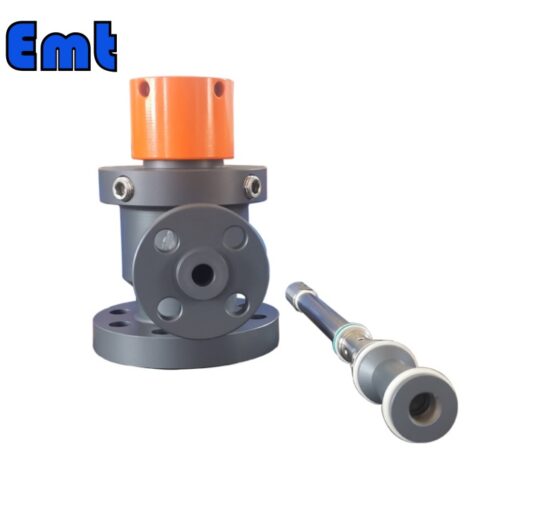
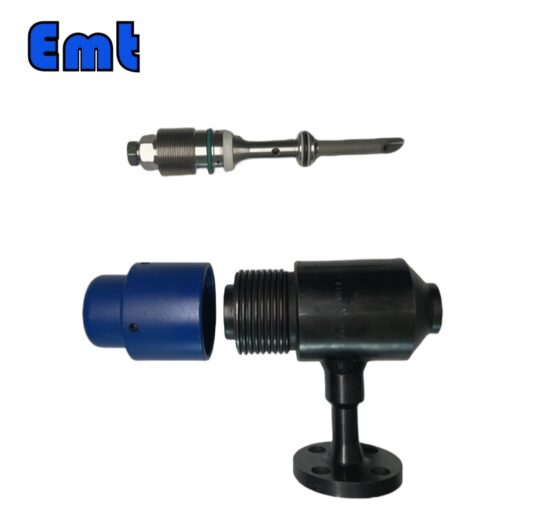
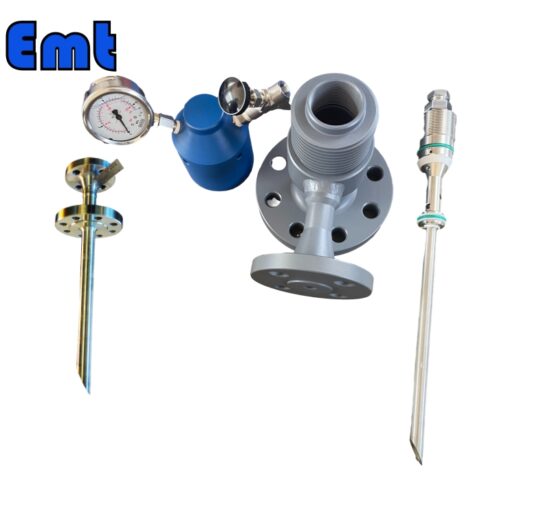
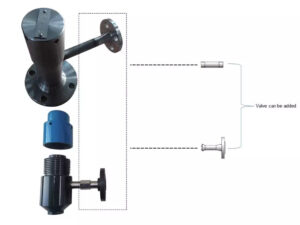
The basic functionality of a quill injector centers on its ability to deliver fluids at controlled rates and specific locations within a system. This targeted delivery facilitates optimal mixing and reaction outcomes, crucial in processes like chemical reactions. Precise proportions and thorough mixing dictate the quality of the final product. The main components defining a quill injector include the injection quill itself, a check valve to prevent backflow, a connection flange for process line attachment, and often, a metering valve to control the injection rate.
Turning to historical development, the origins of quill injectors go back to the mid-20th century. Industries then began to emphasize precision in fluid delivery systems. Initially developed for the oil and gas industry to enhance the injection of corrosion inhibitors and other chemicals, the technology soon found broader applications.
Significant milestones in quill injector technology include integrating advanced materials that withstand corrosive substances and high pressures. This integration has enhanced the durability and reliability of the injectors. The advent of computer-aided design technologies also advanced the precision with which manufacturers could produce these injectors. This allowed for more complex and exacting designs tailored to specific industrial needs.
Moreover, recent advancements have integrated smart technology into quill injectors. These enhancements enable real-time monitoring and control of injection parameters. Smart injectors can now adjust flow rates automatically based on process system feedback. This optimization occurs without manual intervention. This evolution marks a significant leap from their original designs, positioning quill injectors as essential components in modern industrial operations.
Types d’injecteurs de piquants
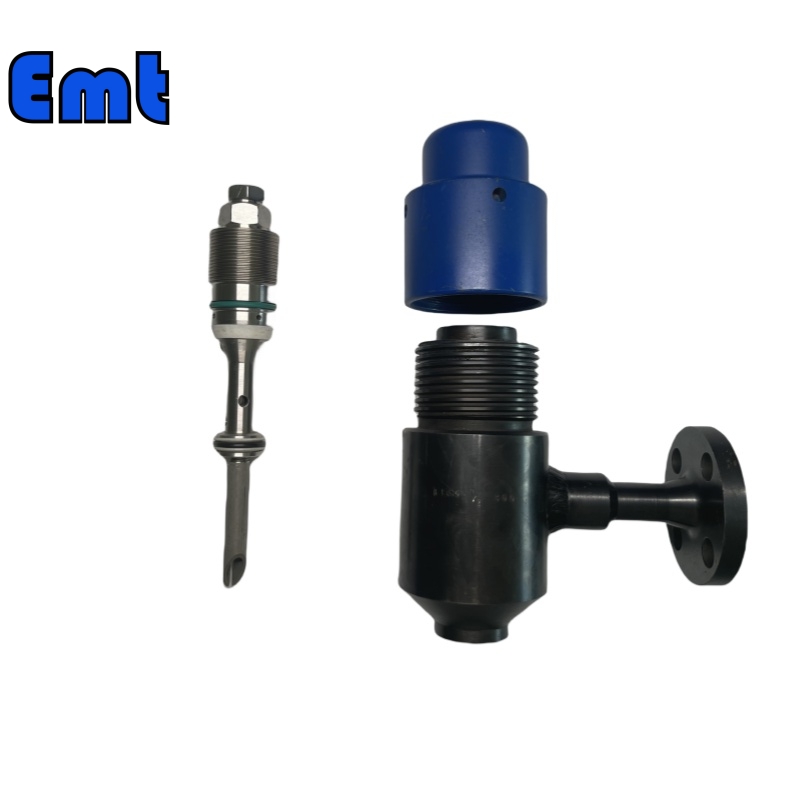
Plume d’injection chimique
Chemical injection quills are meticulously designed to optimize the delivery of chemicals into pressurized systems. They feature a slender tube that extends into the main pipeline, ensuring precise injection at the point of highest fluid turbulence to enhance mixing and reaction efficiency. Typically, operators in the chemical processing industries use these quills for tasks such as pH control, corrosion inhibition, and scale prevention. The design allows for a controlled discharge of chemicals, which is crucial for maintaining process integrity and product quality.
One of the primary advantages of using chemical injection quills in these industries is their ability to deliver exact amounts of chemicals directly into critical areas. This precision reduces chemical wastage and ensures that the entire process remains cost-effective. Furthermore, by improving the accuracy of chemical dosing, these quills help in maintaining stringent safety standards, minimizing the risk of chemical overuse or underuse, which can lead to hazardous situations.
Water Treatment Injector
Shifting the focus to water treatment injectors, these devices play a pivotal role in modern water purification processes. They inject coagulants, disinfectants, and pH adjusters into water systems. This can ensure the water meets safety and quality standards before it reaches consumers or is returned to the environment. Water treatment injectors are specifically tailored to handle the high flow rates and varying pressures typical in water treatment plants, ensuring consistent and effective treatment across all stages of the process.
Unique features tailored for water treatment include materials resistant to corrosion and wear. They are essential given the harsh chemicals often used in water treatment. Additionally, many water treatment injectors are designed to be easily adjustable, allowing for quick changes in injection rates to respond to fluctuating treatment needs. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining optimal water quality and adapting to varying demand levels or incoming water conditions.
In conclusion, both chemical injection quills and water treatment injectors are indispensable tools in their respective fields. Their specific features enhance their functionality and effectiveness in complex industrial processes.








Il n’y a pas encore d’avis.